PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS(01)
2017. 6. 20. kyho@skuniv.ac.kr
1. The signals that guide the allocation of resources in a market economy are
a. surpluses and shortages. b. quantities. c. government policies. d. prices.
2. The smaller the price elasticity of demand, the
more likely the product is a luxury.
smaller the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
more substitutes the product has.
greater the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
3. When the price of a good is $5, the quantity demanded is 100 units per month; when the price is $7, the quantity demanded is 80 units per month. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand is about
a. 0.22. b. 0.67. c. 1.33. d. 1.50.
4. Which of the following causes the price paid by buyers to be different than the price received by sellers?
a. a binding price floor b. a binding price ceiling
c. a tax on the good d. All of the above are correct.
5. Minimum-wage laws dictate
the exact wage that firms must pay workers.
a maximum wage that firms may pay workers.
a minimum wage that firms may pay workers.
both a minimum wage and a maximum wage that firms may pay workers.
6. When a binding price ceiling is imposed on a market,
price no longer serves as a rationing device.
the quantity supplied at the price ceiling exceeds the quantity that would have been supplied without the price ceiling.
all buyers benefit.
All of the above are correct.
7. The particular price that results in quantity supplied being equal to quantity demanded is the best price because it
a. maximizes costs of the seller. b. maximizes the combined welfare of buyers and sellers.
c. minimizes the expenditure of buyers. d. maximizes tax revenue for the government.
8. A demand curve reflects each of the following except the
willingness to pay of all buyers in the market.
value each buyer in the market places on the good.
highest price buyers are willing to pay for each quantity.
ability of buyers to obtain the quantity they desire.
9. Producer surplus is the
area under the supply curve to the left of the amount sold.
amount a seller is paid minus the cost of production.
area between the supply and demand curves, above the equilibrium price.
cost to sellers of participating in a market.
10. A tax on a good
raises the price that buyers effectively pay and raises the price that sellers effectively receive.
raises the price that buyers effectively pay and lowers the price that sellers effectively receive.
lowers the price that buyers effectively pay and raises the price that sellers effectively receive.
lowers the price that buyers effectively pay and lowers the price that sellers effectively receive.
11. The price elasticities of supply and demand affect
both the size of the deadweight loss from a tax and the tax incidence.
the size of the deadweight loss from a tax but not the tax incidence.
the tax incidence but not the size of the deadweight loss from a tax.
neither the size of the deadweight loss from a tax nor the tax incidence.
12. When a country allows trade and becomes an exporter of a good,
domestic producers gain and domestic consumers lose.
domestic producers lose and domestic consumers gain.
domestic producers and domestic consumers both gain.
domestic producers and domestic consumers both lose.
13. Which of the following is NOT a way of internalizing technology spillovers?
a. subsidies b. patent protection c. industrial policy d. taxes
14. An externality
results in an equilibrium that does not maximize the total benefits to society.
causes demand to exceed supply.
strengthens the role of the “invisible hand” in the marketplace.
affects buyers but not sellers.
15. Resources tend to be allocated inefficiently when goods
a. are private goods. b. are rival in consumption and excludable.
c. are available free of charge. d. are available only at very high prices.
16. A corrective tax
allocates pollution to those factories that face the highest cost of reducing it.
is a form of regulation.
works well for all types of externalities.
is inferior to regulatory policy according to most economists.
17. The provision of a public good generates a
positive externality, as does the use of a common resource.
positive externality and the use of a common resource generates a negative externality.
negative externality, as does the use of a common resource.
negative externality and the use of a common resource generates a positive externality.
18. Tradable pollution permits
have prices that are set by the government.
will be more valuable to firms that can reduce pollution only at high costs.
are likely to create a higher level of total pollution.
are less desirable than corrective taxes in reducing pollution.
19. Each of the following explains why cost-benefit analysis is difficult except
there is no price with which to judge the value of a public good.
surveys are often biased and unreliable.
it is difficult to identify all factors that influence costs and benefits of public goods.
government projects rarely have sufficient funding to complete them on time.
20. Which of the following is not a way for the government to solve the problem of excessive use of common resources?
a. regulation b. turning the common resource into a public good
c. taxes d. turning the common resource into a private good
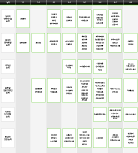
21. Fill in the following table, and explain why.
| A Decrease in Supply | An Increase in Supply | No Change in Supply |
A Decrease in Demand | P : Ambiguous Q : Down | ① | P : Down Q : Down |
An Increase in Demand | ② | ③ | ④ |
No Change in Demand | P : Up Q : Down | ⑤ | P : Same Q : Same |